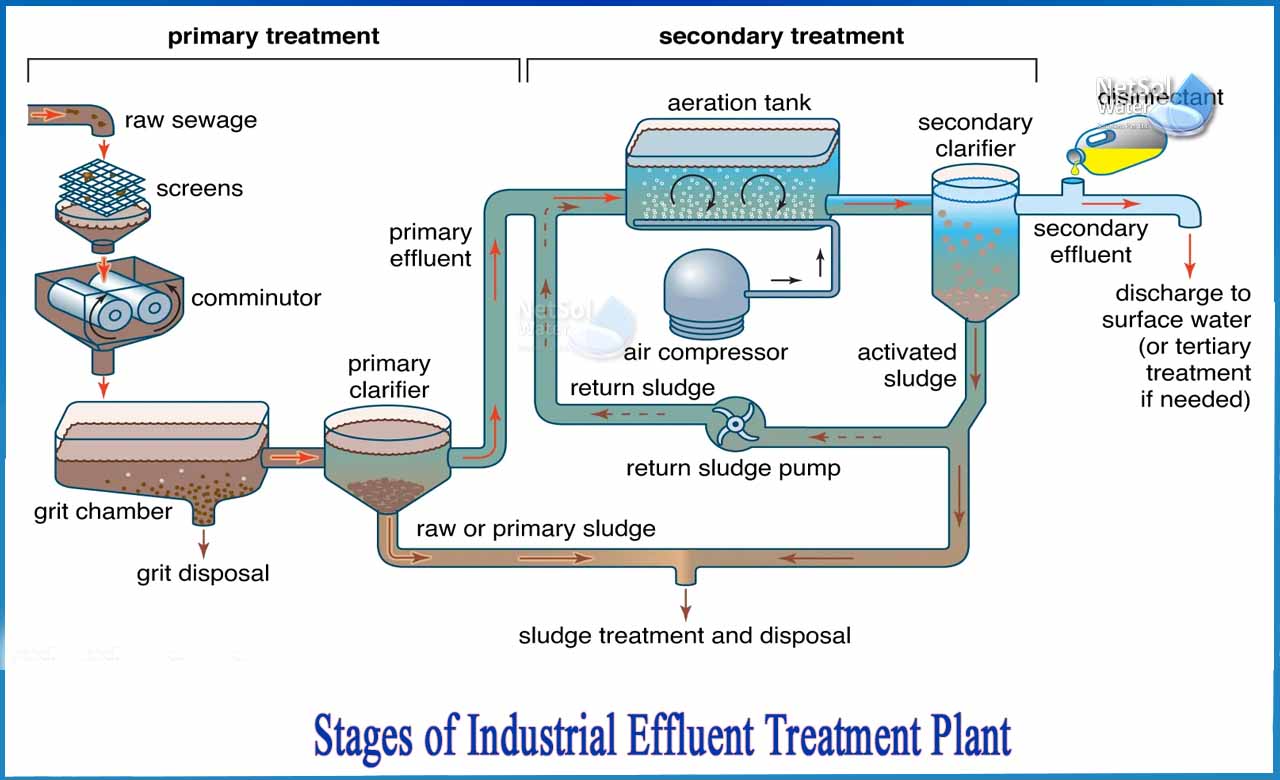
Key Methods in Industrial Waste Water Treatment Processes
The therapy of industrial wastewater is a vital aspect of ecological management, involving a variety of strategies developed to alleviate the impact of impurities. Developments in modern technologies such as membrane layer filtering and advanced oxidation processes use cutting-edge options for boosting treatment efficacy.
Physical Treatment Methods
Just how effectively can physical therapy methods address the intricacies of industrial wastewater? Physical treatment techniques play a pivotal role in the preliminary stages of wastewater monitoring, focusing largely on the removal of solids and large particulates. Strategies such as filtration, flotation protection, and sedimentation are essential for lowering the concentration of put on hold solids, therefore boosting the efficiency of subsequent therapy processes.
Sedimentation entails the gravitational settling of solids, enabling for the separation of heavier products from the wastewater. This technique is particularly effective in clearing up water before chemical or biological treatments. Filtering, on the other hand, makes use of numerous media to catch particulate matter, guaranteeing that smaller impurities are gotten rid of. This strategy can be customized to fit different kinds of industrial effluents, generating more clear effluent streams.
Additionally, flotation protection approaches, which make use of air bubbles to lift put on hold solids to the surface area for removal, work in treating wastewater with high focus of fats, oils, and oils. Generally, physical therapy techniques function as a vital primary step in the thorough management of industrial wastewater, making sure that the lots on succeeding treatment phases is lessened and improving total therapy efficacy.
Chemical Treatment Methods
While physical therapy approaches prepared for reliable wastewater monitoring, chemical therapy strategies are essential for addressing the much more complicated contaminants commonly found in commercial effluents. These approaches utilize different chemical representatives to precipitate, reduce the effects of, or oxidize hazardous substances, guaranteeing a more detailed elimination of pollutants.
One common method is coagulation and flocculation, where chemical coagulants such as light weight aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride are contributed to promote the gathering of put on hold bits. This procedure boosts solid-liquid separation, reducing turbidity and enhancing water quality. In addition, neutralization procedures are used to adjust the pH of wastewater, utilizing bases or acids to neutralize acidic or alkaline streams, specifically.
Oxidation-reduction responses play an important function in degrading organic contaminants and microorganisms. Chemical oxidants like hydrogen, ozone, or chlorine peroxide are utilized to damage down complex organic compounds, making them less unsafe or a lot more naturally degradable. Progressed oxidation procedures (AOPs) combine multiple oxidation methods to improve pollutant removal performance.
Biological Treatment Procedures
The effectiveness of wastewater treatment is dramatically improved by organic treatment processes, which harness the natural metabolic tasks of bacteria to disintegrate raw material and remove pollutants. Industrial Waste Water Treatment. These procedures primarily include aerobic and anaerobic food digestion, each customized for specific kinds of wastewater
Aerobic treatment procedures use oxygen to support microbial growth, advertising the breakdown of natural contaminants right into co2 and water. Typical techniques include triggered sludge systems, where oygenation containers assist in the mixing of wastewater with microorganisms, and flowing filters, which encourage biofilm growth on media surfaces.
Alternatively, anaerobic treatment processes happen in the absence of oxygen, utilizing anaerobic bacteria to break down natural matter, causing biogas More Help production, a renewable resource source. Anaerobic digesters are commonly employed in industrial settings for this purpose, efficiently lowering the quantity of sludge while generating useful biogas.
The choice of a biological treatment technique depends upon wastewater features, therapy objectives, and governing criteria. The integration of organic processes in wastewater treatment not only improves toxin removal effectiveness but additionally advertises sustainability by reducing chemical use and supporting resource recuperation.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Usual AOP methods include Fenton's ozonation, reagent, and photocatalysis. Fenton's reagent, a combination of hydrogen peroxide and ferrous iron, catalyzes the formation of hydroxyl radicals, making it reliable for treating wastewater having phenolic compounds and other stubborn compounds. Ozonation uses ozone as an effective oxidant, efficient in deteriorating a wide variety of natural pollutants while all at once sanitizing the effluent. Photocatalysis employs light-activated stimulants, such as titanium dioxide, to improve oxidation responses and get rid of impurities.
AOPs offer a number of benefits, consisting of lowered sludge production and the ability to treat wastewater with high concentrations of natural contaminants. The execution of AOPs requires careful consideration of functional parameters and cost-effectiveness, ensuring that these innovative strategies are suitably integrated into existing wastewater therapy systems.
Membrane Layer Filtering Technologies

Microfiltration is reliable for removing put on why not look here hold bacteria and solids, while ultrafiltration targets smaller natural particles and infections. Nanofiltration bridges the space in between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis, efficiently getting rid of organic substances and divalent ions. Reverse osmosis supplies the highest degree of filtration, utilized largely for desalination and removing mono-valent ions.
Membrane innovations supply various advantages, including low energy intake compared to traditional therapy methods, modular style for scalability, and the possibility for water healing and reuse. However, difficulties such as membrane layer fouling and the requirement for routine upkeep must be dealt with to make certain system efficiency. In general, membrane filtration modern technologies stand for a vital element of modern industrial wastewater therapy strategies, promoting sustainability and source preservation in water administration.
Final Thought
In conclusion, industrial wastewater therapy uses a varied selection of strategies, consisting of physical, chemical, biological, and advanced approaches. Proceeded improvements in these methodologies will even more enhance the efficiency and efficiency of wastewater therapy processes in industrial setups.
The treatment of industrial wastewater is a critical element of ecological management, involving a variety of techniques designed to reduce the influence of impurities.Exactly how efficiently can physical treatment techniques address the intricacies of commercial wastewater?Advanced oxidation procedures (AOPs) stand for a cutting-edge approach in industrial wastewater therapy, created to effectively weaken natural pollutants that are often resistant to traditional treatment techniques (Industrial Waste Water Treatment).In final thought, commercial wastewater therapy utilizes a diverse range of techniques, including physical, chemical, organic, and advanced methods. Continued developments in these methodologies check my reference will further boost the effectiveness and effectiveness of wastewater treatment processes in industrial settings